Grid Computing at Creatis
Grid Computing Projects
Grid Computing at Creatis
The CREATIS laboratory has been involved for many years in research activities dealing with grids and their usage for biomedical applications. Grid Computing at Creatis involves both engineering and research activities.
1. Application porting on the EGEE Grid
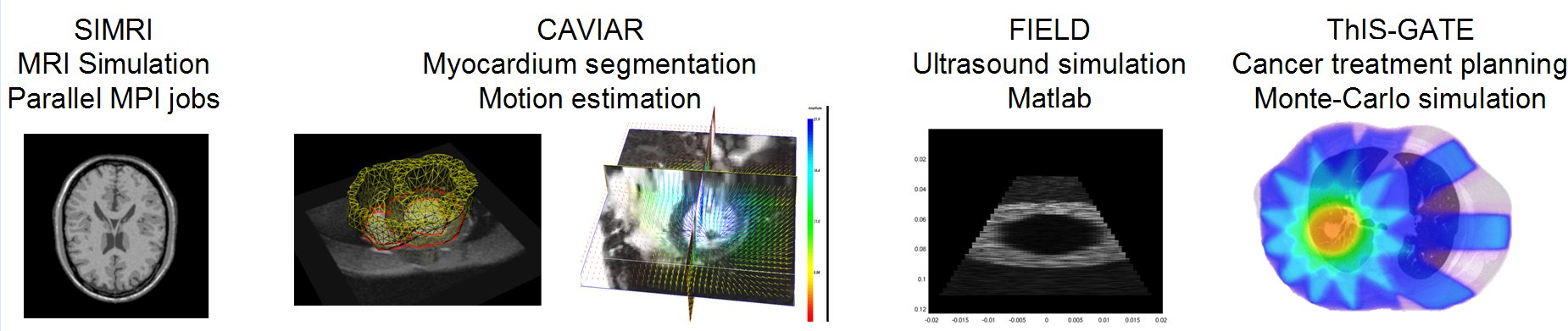
SIMRI3D
Simri is a versatile and interactive 3D MRI simulator. Based on the Bloch equations, it includes an efficient management of the T2* effect. It takes into account the main static field value and enables realistic simulations of the chemical shift artifact including off-resonance phenomena. It also simulates the artifacts linked to the static field inhomogeneity like those induced by susceptibility variation within an object. It is implemented in the C language and the MRI sequence programming is done using high level C functions with a simple programming interface. To manage large simulations, the magnetization kernel is implemented in a parallelized way (with MPI) that enables simulation on cluster and grid architectures.
CAVIAR
The CAVIAR application deals with motion estimation and 3D segmentation of the cardiac muscle (myocardium) in MRI series.
ThIS/GATE
ThIS is a Therapeutic Irradiation Simulator for cancer therapy which is now being integrated into the OpenGATE project. It computes the 3D dose distribution resulting from an irradiation with carbon ion beams. The simulator has been ported on the EGEE Grid for computational speed-up. The porting methodology was presented at EGEE’08 Istanbul. The poster presented is available here.
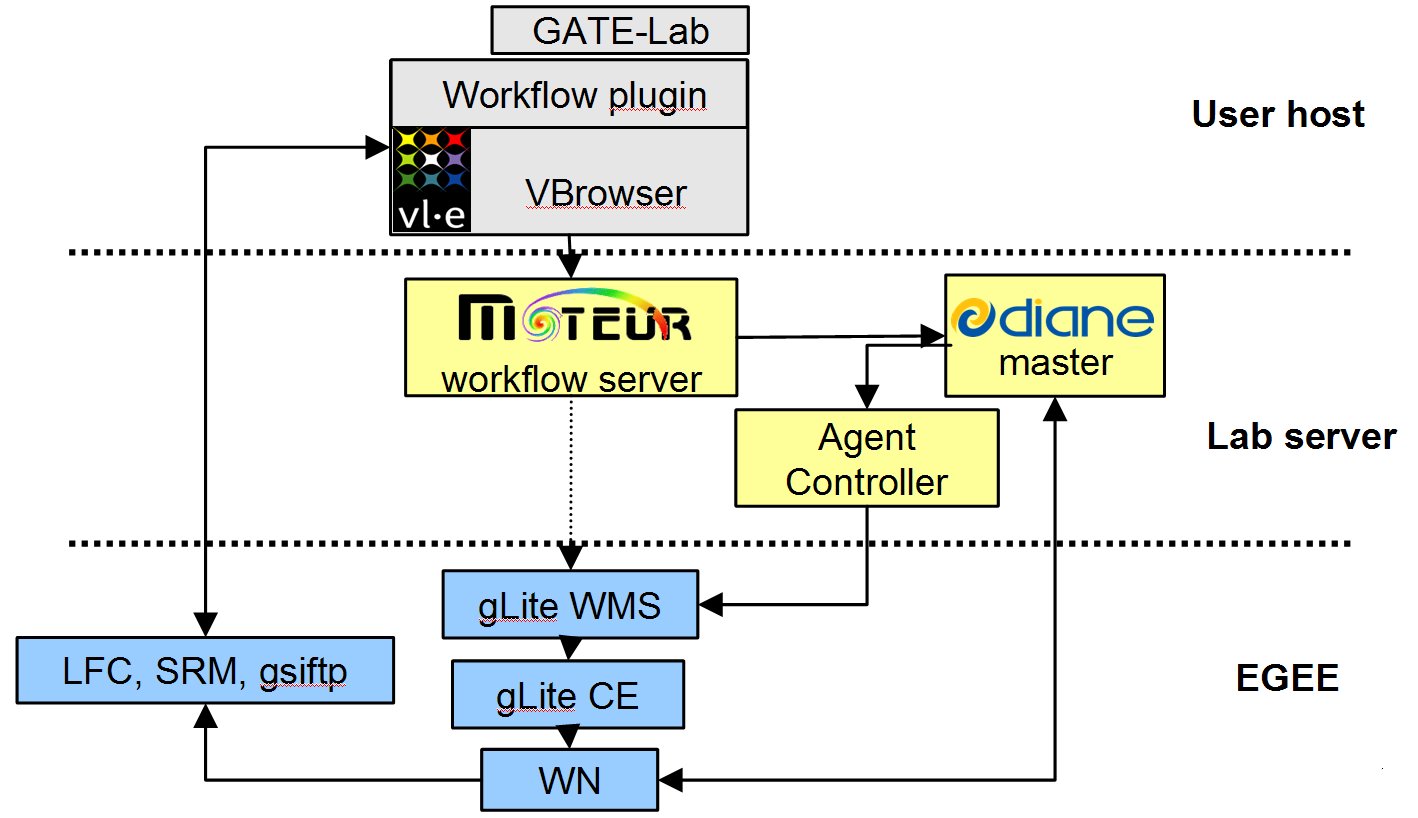
2. Porting and execution environment
The porting environement is described below. Is has been created in collaboration with CNRS-I3S, CERN and UVA.
3. Modelling
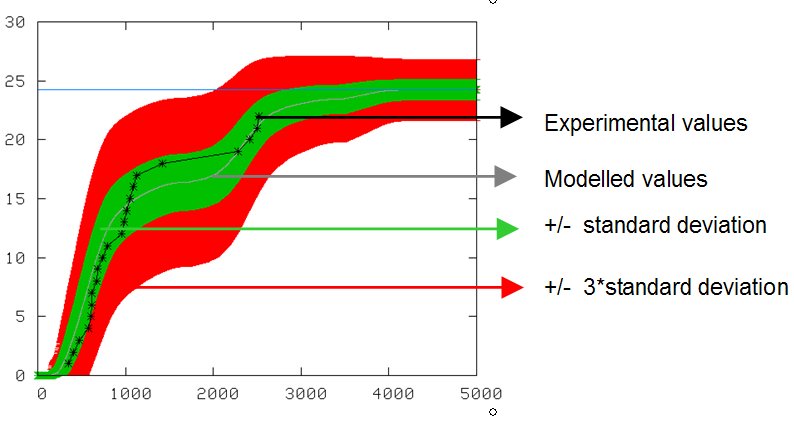
Modelling the behaviour of medical imaging applications on the grid helps improving their performance.
4. Optimization
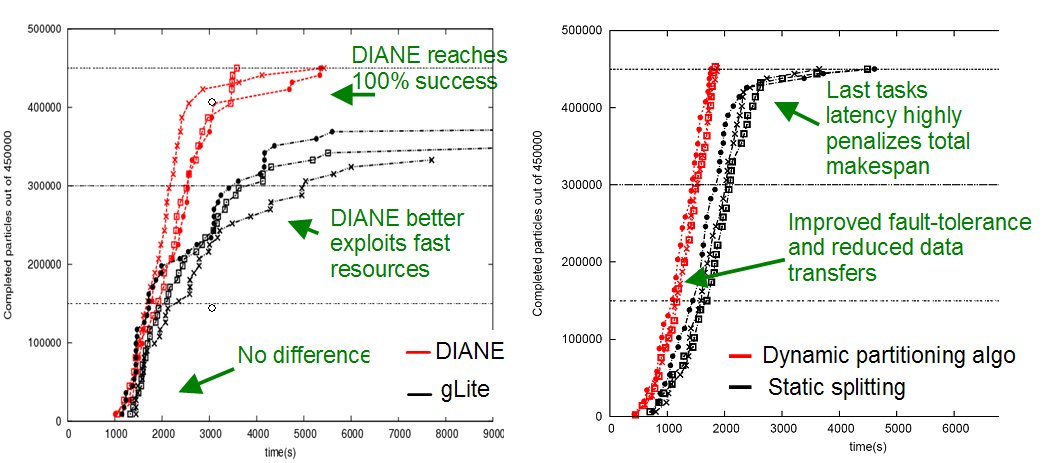
Improving performance and QoS by using different techniques:
- pilot jobs (left hand side figure)
- new partitioning algorithms (right hand side figure)
Grid Computing Projects
Computing Grids are nowadays spreading and evolving rapidely. There are already several national grid initiatives (NGI) in several countries like the United Kingdom (UK National Grid), Germany (D-Grid), Greece (HellasGrid), Italy (INFN Italian National Grid), Holland (DutchGrid), or Japan (NAREGI). In France the French National Grid Institute (Institut National des Grilles -IdG) has been active since december 2007.
There are also larger grids gathering several contries or even continents. A few exemples are the Open Science Grid (United States and Asia), NorduGrid (Northern Europe) or EGEE (european grid exented recently to Asia and Africa).
EGEE
The EGEE (Enabling Grid for E-science in Europe) grid is currently the largest production grid worldwide providing more than 40,000 CPUs and several Petabytes of storage. This infrastructure is used on a daily basis by thousands of scientists organized in over 200 Virtual Organizations (VOs). EGEE is operated by the gLite middleware, which provides high-level services for scheduling and running computational jobs, as well as for data and grid infrastructure management. CREATIS has been involved in this project from the every beginning and has actively participated in the NA4 group in charge of application porting and user support.