Context
The joint analysis of images generated from different MR sequences (multi-parametric MRI or mp-MRI) has been shown to allow non-invasive discrimination and localization of prostate cancer (Pca) which may open the way to targeted biopsy or active screening of patients with non aggressive cancer lesions. Integrating the large amount of visual information provided by the different MR sequences, however, is complex, especially for junior radiologists with less expertise.
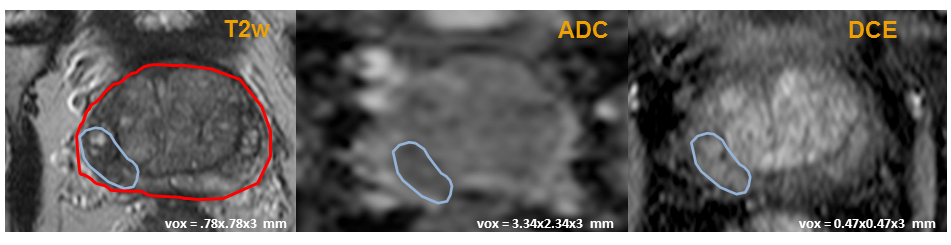
Fig 1. Prostate MRI: (left) axial T2-w, (middle) DCE (45 s after Gd-DOTA injection) and (right) ADC MR images obtained on a patient with superimposed delineation of the prostate gland (red) and of a suspicious region of interest (blue).
Objective
The purpose of this project is to develop a computer aided decision system (CAD) that prospectively performs automatic discrimination between suspicious but normal prostate tissue and cancer lesions of different level of aggressiveness (indexed by Gleason score) in mp-MRI of prostate cancer patients. The first phase was to build a system able to evaluate the malignancy degree of suspicious locations outlined by the radiologist. The training and evaluation datasets consisted of thirty 1.5 Tesla multiparametric MR imaging studies (with T2-weighted, diffusion-weighted (ADC), and dynamic contrast material–enhanced (DCE) imaging, as shown on Fig1 above) of the CLARA-P database developed by Pr O. Rouvière (HCL, Lyon) obtained before radical prostatectomy in patients between September 2008 and February 2010. This resulted in a series of 42 cancer regions of interest (ROIs) and 49 benign but suspicious ROIs.
Results
We have developed an original CADx system based on an optimized set of 34 statistical, textural and functional features (selected among 140 initial features by using filter methods) and a support vector machine classifier using a Gaussian kernel [Niaf et al, PMB 2012] . For every outlined lesion, the CAD system computes a likelihood of malignancy ranging from 0 (definitely benign) to 1 (definitely malignant). The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) for the stand-alone CAD system on the study population was estimated at 82% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 73%, 90%). This system was also shown to improve the diagnostic performance of junior and senior radiologists in scoring prostate lesions by increasing reading specificity [Niaf et al, Radiology 2014].
Current research focuses on the second phase of the project which consists in developing a CAD system that generates probability scores of malignancy at a voxel level (probability maps) in the whole prostate [Lehaire et al, ICIP 2014].
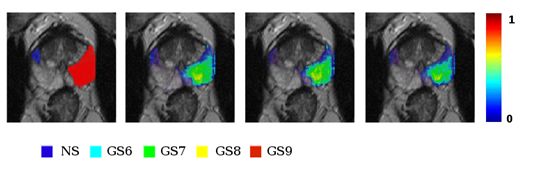
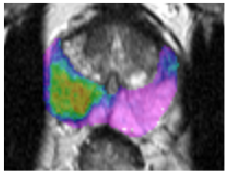
Fig 2. Example transverse slice of a patient with two outlined lesions, a suspicious but benign lesion in blue and a very aggressive cancer (Gleason score of 9) in red. Second to last column: corresponding probability maps generated by 3 different CAD schemes
Collaboration
O. Rouvière, HCL, Lyon
This project was funded by two INCa’s grants: Cartographix (2011-14) and LYRIC (2012-17)