Problem and context
Fast segmentation of 3D organs is a strongly needed step in many clinical applications. Our goal is to
developed an efficient framework well adapted for the accurate segmentation of anatomical structures
in medical imaging, with a particular interest for the left ventricle of the heart
Methods, contributions and results
We have introduced an novel variational segmentation framework which allows performing near real time segmentation of 3D anatomical structures. This method, named B-spline Explicit Active Surface (BEAS), corresponds to a variational active surface formalism strongly inspired by the classical level-set method
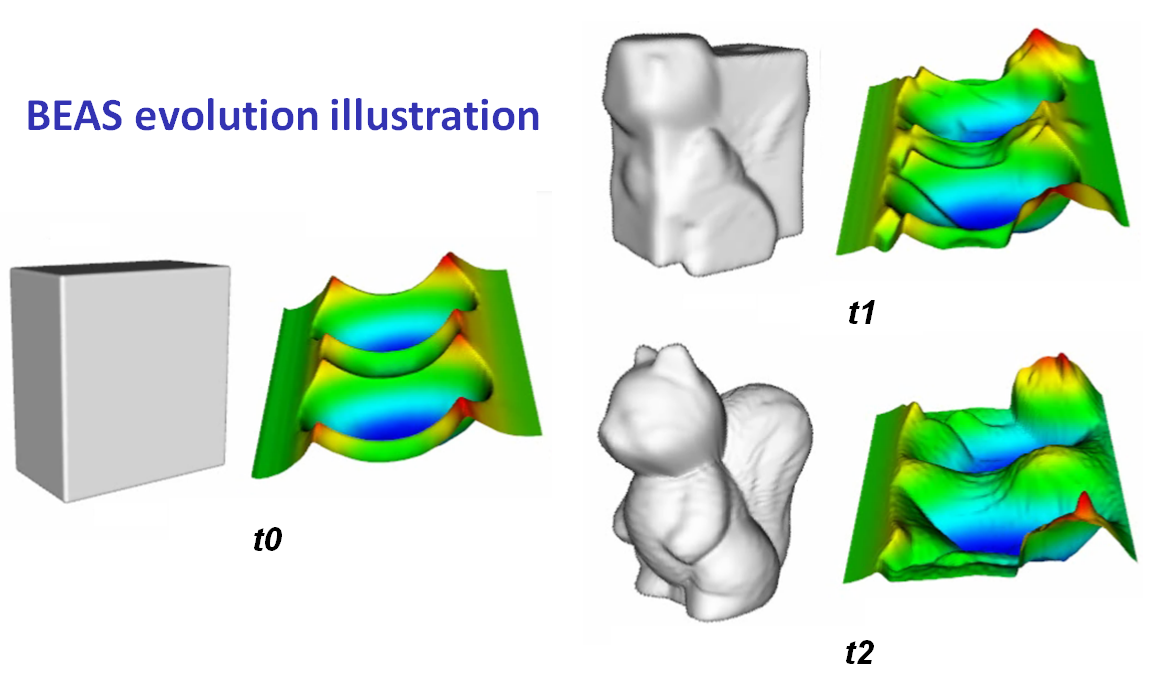
Figure 1 Three iteration steps of the algorithm segmenting a 3D squirrel. (t0) initialization, (t1) intermediate step, (t2) final result at convergence.
The evaluation of our method as part of the Challenge on Endocardial Three-dimensional Ultrasound Segmentation (CETUS challenge, MICCAI 2014) has shown that it ranks first in the automatic segmentation category based on the analysis of 30 patients over the 5 automatic methods which have been evaluated
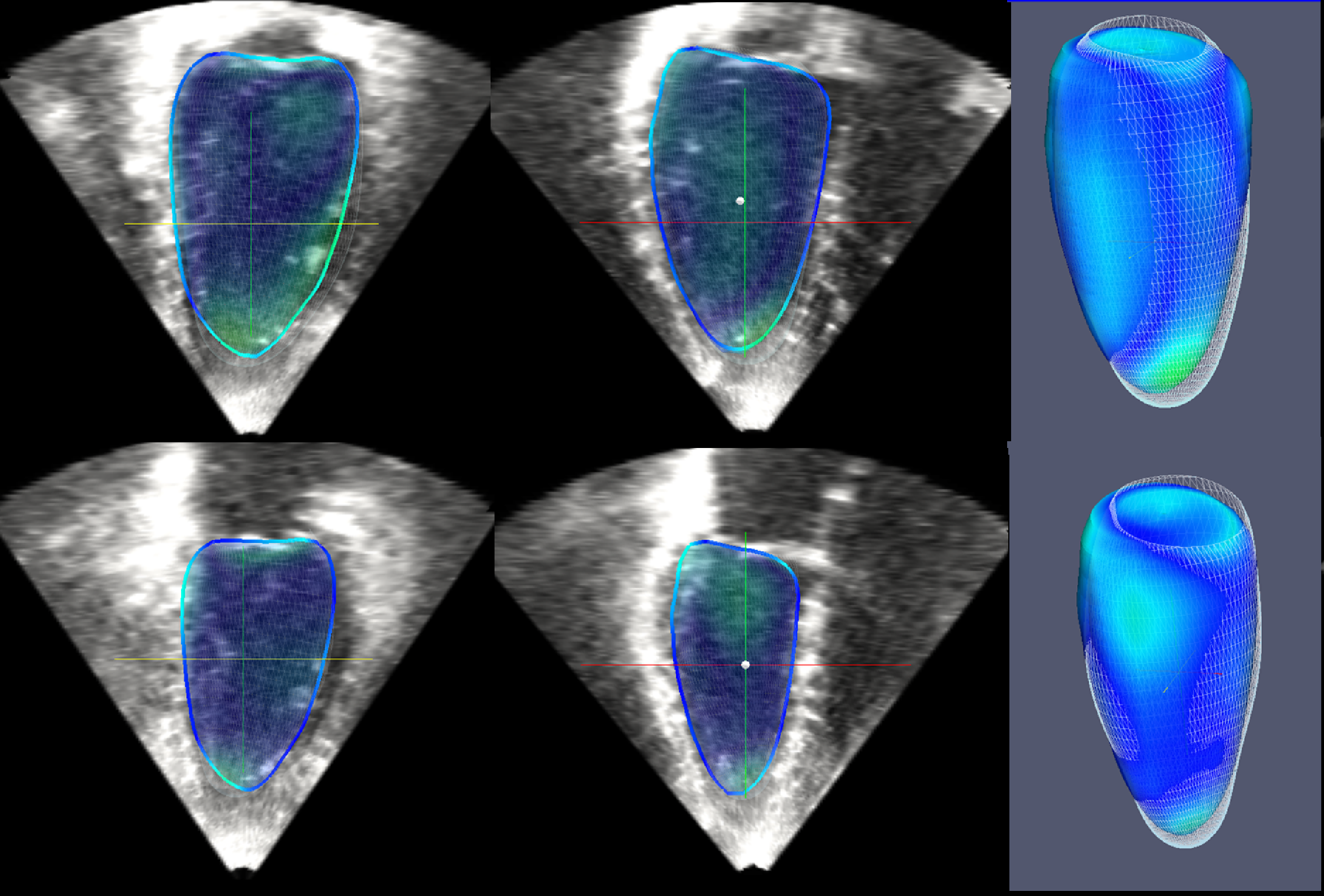
Figure 2 Top row: segmentation of the end-diastolic phase (Mean absolute distance error = 1.04mm). Bottom row: segmentation of the end-systolic phase (Mean absolute distance error = 1.69mm).