Context
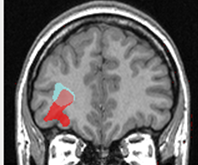
The analysis of neuroimaging data such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) is increasingly used in the pre-surgical work-up of patients suffering from epilepsy and may offer an alternative to the invasive reference of Stereo-electro-encephalography (SEEG) monitoring. Integrating the large amount of visual information provided by the multiparametric and multimodality data, however, is complex, especially for junior neurologists with less expertise.
Objective
To assist clinicians in screening these lesions, we developed a computer aided diagnosis system (CAD) based on a multivariate data analysis approach. Our first contribution was to formulate the problem of epileptogenic lesion detection as an outlier detection problem. The main motivation for this formulation was to avoid the dependence on labelled data and the class imbalance inherent to this detection task. The proposed system builded upon the one class support vector machines (OC-SVM) classifier. OC-SVM was trained using features extracted from MRI scans of healthy control subjects, allowing a voxelwise assessment of the deviation of a test subject pattern from the learned patterns. System performance was evaluated using realistic simulations of challenging detection tasks as well as clinical data of patients with intractable epilepsy.
Results
Supplementary material of the paper may be found here
Collaboration
A. Hammers, King's College, London
Julien Jung, CRNL, Lyon
This project is part of Meriem El Azami's PhD and was funded by the Labex PRIMES.