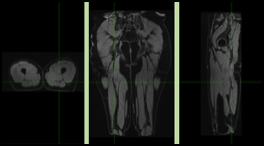
Micro-structural and functional modifications induced by Ultra-endurance at the level of skeletal muscles and myocardium, as well as inflammation generated by such extremes training conditions, have never been explored using Magnetic resonance Imaging (MRI).
Post-extreme exercice recovery, and especially the redistribution of water into exercised muscles and myocardium has never been scrutinized coupling the exploration of both myocardium and skeletal muscles, and using advanced MRI techniques including spectroscopy. Recent developments in quantitative functional MRI allow us to envisage non-invasive and longitudinal exploration prior, during and after ultra-trail, with unmatched anatomical and functional investigation of cardiac and skeletal muscle.
Several MRI and ultrasound studies have shown the existence of functional and biochemical alterations in the myocardium after prolonged intense sport performances. Published US studies (Nottin Circ 2009) demonstrated systolic and diastolic transient dysfunctions: decreased global and regional LV function, regional deformation abnormalities with an increased ventricular torsion.
US elastography allows uniquely to visualize and measure soft tissues stiffness. This new imaging method will provide additional informations
Our hypothesis is that inflammatory phenomena caused by the ultra-endurance are responsible of functional disorders observed after the end of the running performance. This study should allows to identify and fully characterize a new model of human tissue stress, in regard to inflammatory levels that are close to those observed in severe ill conditions such as in intensive care units in multiple traumatic injuries or after myocardial infarction. By testing innovative quantitative imaging methods and new non-invasive bio-markers, in conditions close of those met with severe ill patients, (hence difficult to include in clinical trials), will accelerate the transfer and the validations of newly developed methodology. Moreover, thanks to MRI, this study will provide new insights into the physiological mechanisms involved during ultra-endurance, at the cardiac and muscular level, but also during the recovery process. Therefore, beyond to a deeper understanding of ultra-endurance’s impact, this project aims to validate, improve, and test the performance of newly available imaging indicators, foreseen to be deployed at short-term in the evaluation of innovative strategies for organs protection.
Ultimately, this work will help to better care of diseases and conditions with strong public health impact.
This study has several goals and recipients : -for the doctor, this project will offer new methodologies and their validations for patients care. -for the patient since he will benefit from improved solutions and treatment followup by imaging. -for the runner, the project will provide new insigths on muscle physiology in such extreme conditions. This study will also increase the visibility abroad for the partners and for the territory.
Finally, care was also taken to promote the technology and the methodology developed or enrolled in this project toward the people.